The Bihar Public Service Commission (BPSC) has recently unveiled the syllabus and pattern for the Headmaster exam on its official portal. Aspiring candidates are advised to acquaint themselves with the latest syllabus and devise a study plan accordingly. The BPSC Headmaster exam syllabus encompasses two subjects: general studies and questions related to B.ED. It is crucial for candidates to thoroughly review the syllabus to enhance their preparation and strategize their study approach for the upcoming BPSC Headmaster Recruitment test in 2024.
| BPSC Headmaster Syllabus 2024 Overview | |
| Exam Conducting Body | Bihar Public Service Commission |
| Exam Name | Headmaster |
| Vacancies | 6061 |
| Category | BPSC Headmaster syllabus and exam pattern 2024 |
| Selection Process | Written Exam and Interview |
| Maximum Marks | 150 |
| Duration | 2.5 Hours |
BPSC Headmaster Syllabus 2024 for General Studies
Here is the detailed BPSC Headmaster syllabus 2024 for general studies, shared below for the reference of the aspirants.
- General Science.
- Current events of national and international importance
- History of India and salient features of the history of Bihar
- Indian National Movement and the role played by Bihar.
- Geography
- Indian Polity
- Indian Economy
- Elementary Mathematics and Mental ability test
Advertisement
BPSC Headmaster Syllabus 2024 for B.Ed
Here is the detailed BPSC Headmaster syllabus 2024 for B.Ed-related questions shared below for the reference of the aspirants.
Unit 1
- Understanding Childhood
- Children and their childhood:
- Dimensions of individual development:
- Adolescence
- Factors affecting adolescence
- The contextual reality of adolescence in Bihar
Advertisement
Unit 2
- Socialisation and the context of school
- Inequalities and resistance in society
- Differences in learners based on socio-cultural contexts
- Understanding differently-abled learners
- Methods of assessing individual differences
Unit 3
- Understanding of Identity Formation
- School as a site of identity formation in teachers and students
- Concepts, meanings, and definitions of education
- Constitutional provisions on education that reflect National ideals
- Education for National development
Advertisement
Unit 4
- Philosophy and Education
- Philosophical systems
- Indian Thinkers
- Western Thinkers
Unit 5
- Meaning of equality and constitutional provisions
- Prevailing nature and forms of Inequality, including dominant and minor genders, and related issues
- inequality in schooling
- Differential quality in schooling
- Right to Education
Advertisement
Unit 6
- Concept & Nature of Learning
- Basic Assumptions and analysis of the relevance of Learning Theories Social, Cognitive & Humanistic learning theories
- Learning as a process of construction of knowledge: a constructivist approach to learning
- Relationship of learning with school performance and ability of the learner
- Concept of Motivation
- Forgetting classroom learning-meaning and its causes;
- Meaning of learning to learn skills; ways of developing self-study
Advertisement
Unit 7
- An analysis of teacher’s roles and functions, skills and competencies in the Pre-active phase
- Characteristics associated with effective teachers
- Visualising
- Decision making on outcomes
- preparing for instruction
- Preparation of a plan, Unit plan and Lesson plan
Unit 8
- Motivating the learners and sustaining their attention-importance of stimulus variation and reinforcement as skills.
- questioning Illustration and explanation as teacher competencies influencing student learning in the classroom;
- Strategy of Teaching
- Approaches to Small Group and Whole group Instruction
Unit 9
- How children learn a language, with special reference to Skinner, Chomsky, Piaget and Vygotsky.
- The social and cultural context of language
- Political context of language
- Language and construction of knowledge
- Critical review of Medium of Instruction
- Position of Languages in India; articles 343–351, 350A
Unit 10
What are academic disciplines – Need/Perspectives of the classification of Human knowledge into disciplines & Subjects-
- The Philosophical Perspective: Unity and plurality
- The Anthropological Perspective: Culture and Tribes
- The Sociological Perspective: Professionalisation and Division of Labour
- The Historical Perspective: Evolution and Discontinuity
- The Management Perspective: Market and organisation
- The educational Perspective: Teaching and Learning
- Research in subject/discipline:
- What is interdisciplinary learning?
- What criteria can be used for quality assurance of interdisciplinary subjects?
Unit 11
- Equity and equality in relation to caste, class, religion, ethnicity, disability and region
- Paradigm shift from women’s studies to gender studies
- Historical background
- Gender, culture and institution
- Teacher as an agent of change
- Methods, Inductive deductive, lecture, discussion, multilingual, source method,’observation method, laboratory method, project and problem-solving method and their advantages, limitations & comparisons
Unit 12
- Determinants of the curriculum at the national or statewide level
- The concept of the test, measurement, examination, appraisal, and evaluation and their inter-relationships Purpose and objectives of assessment-for placemen! providing feedbacks’ grading promotion, certification, and diagnostic of learning difficulties
- Reporting student’s performance- progress reports, cumulative records’ profiles and their uses, and portfolios.
- Concepts of inclusive school infrastructure and accessibility, human resources’ attitudes to disability, whole-school approach, and community-based education
- Concept of health, importance, dimensions and determinants of health; Health needs of children and adolescents, including differently-abled children
- Understanding Peace as a Dynamic Social Reality
- Developing Resources in Schools for Guidance
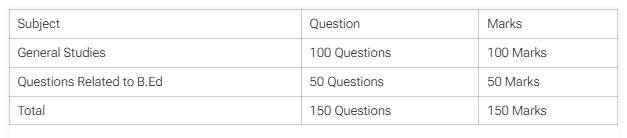
Weightage of BPSC Headmaster Syllabus 2024
Candidates should check the BPSC Headmaster exam pattern 2024 to gain in-depth details about the exam format, number of questions, and marking scheme prescribed in the advertisement. Let’s discuss the weightage of the BPSC Headmaster syllabus 2024 tabulated below.
- The written exam comprises objective-type questions.
- The exam duration will be 2 hours.
- As per the marking scheme, 1 mark will be awarded for each correct answer and there is no provision of negative marking.
| Subject | Question | Marks |
| General Studies | 100 Questions | 100 Marks |
| Questions Related to B.Ed | 50 Questions | 50 Marks |
| Total | 150 Questions | 150 Marks |

Hello Friends, I am from India. After earning my Graduate degree in Computer Application, I decided to pursue my passion for Web Designing and Content Writing. My ultimate goal is to become one of the best in my field and continue to deliver high-quality content. Further, I aim to deliver the latest information regarding recruitment to job seekers, the latest news with accuracy, which shall benefit them in every way possible.